愈创木 Guaiacwood
拉丁学名|Guaiacum officinale
主要产地|巴拉圭
原料分类|木质系列
原料规格|500g-25kg 详情请咨询业务
萃取部位|木质
萃取方式|蒸馏
植物科别|蒺藜科
植物气味|深沉的木质香气,却又带有香草泥土味
▎精油简介
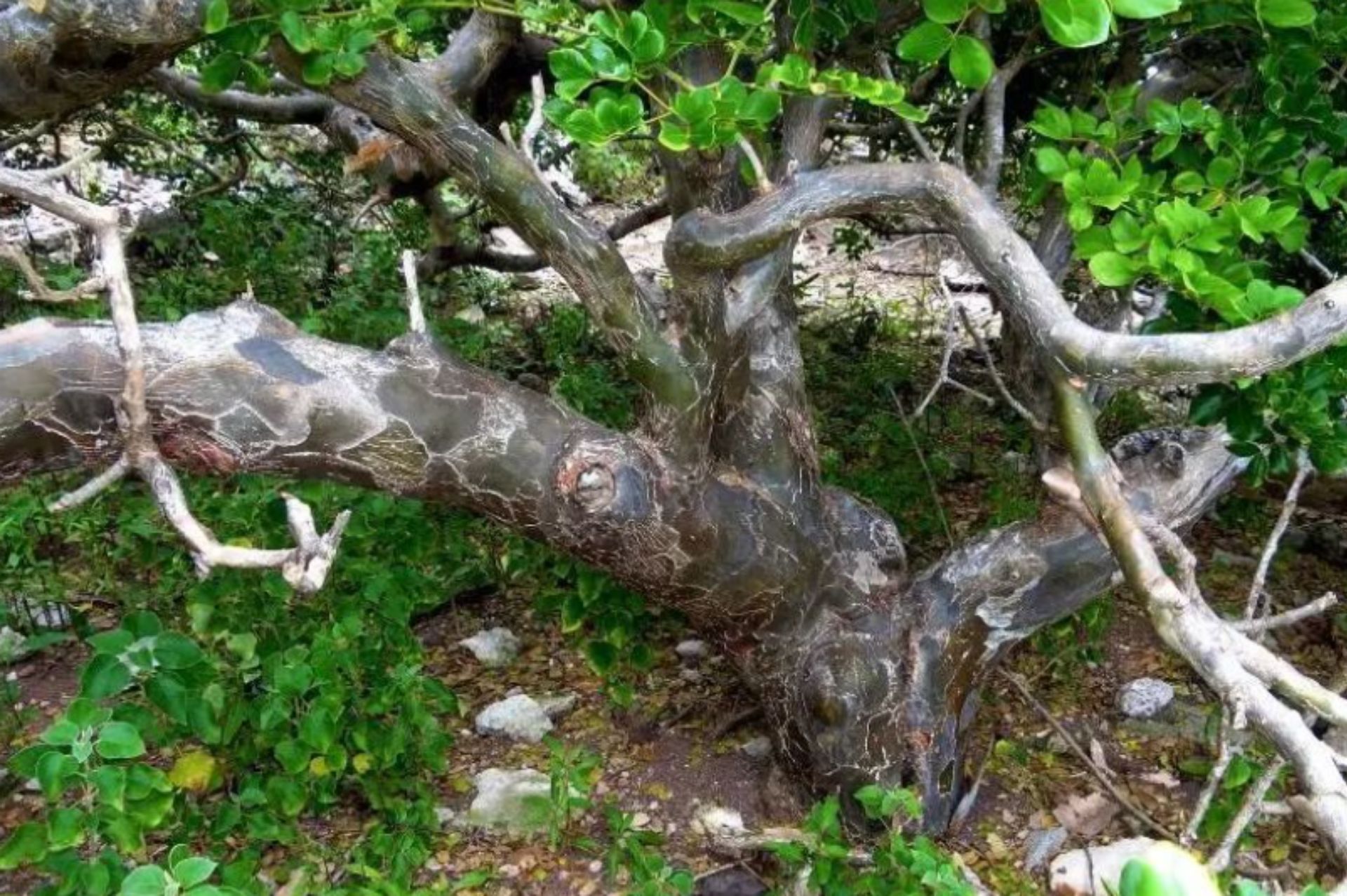
愈创木英文名称源自拉丁文Lignum Vitae,直接翻译就是「生命之树」或「生命之木」,许多古书称为健康树或健康香脂,其生长于南美,阿根廷最多,格兰查科省(Gran Chaco)与里约热内卢(Rio Berjamo),巴拉圭次之,也生长于加勒比海区,是巴哈马的国树,花朵则是牙买加的国花。
它可以长到高达6米左右,有许多弯曲的树枝,呈圆拱形,花朵为蓝色,会结出一串串五到十朵的腋生花束,果实是肉质、呈橘色,有非常坚实质密的树皮,因此不会腐烂,大多数芳香疗法所使用的就是这个部位。愈创树心材并经蒸气蒸馏制成精油,其中主要的有效成分是愈创木酚。
愈创树其天然植物胶可以用来治疗病毒,促进发汗,消炎止痛,根部则能代谢尿酸,茎部有排湿排毒的功效,它还可以作为食品添加剂,香水定香剂。近几年兴起大名鼎鼎的药用成分愈创酚成分其实是来自于这类树种的树脂内,这个成分也能在烘培的咖啡豆中找得到,更是许多熏制食品的前趋物。原生植物体有如此丰富的愈创酚,但却在愈创木精油中仅珍贵的少量。
▎成分解析
|主要成分:单萜醇
主要成分为愈创木醇、愈创木酚、α-愈创甘油醚、β-广藿香烯、愈创木氧化物。
|研究认证

▸ 研究显示愈创木对实验诱发的雄性白化大鼠具有保肝作用。
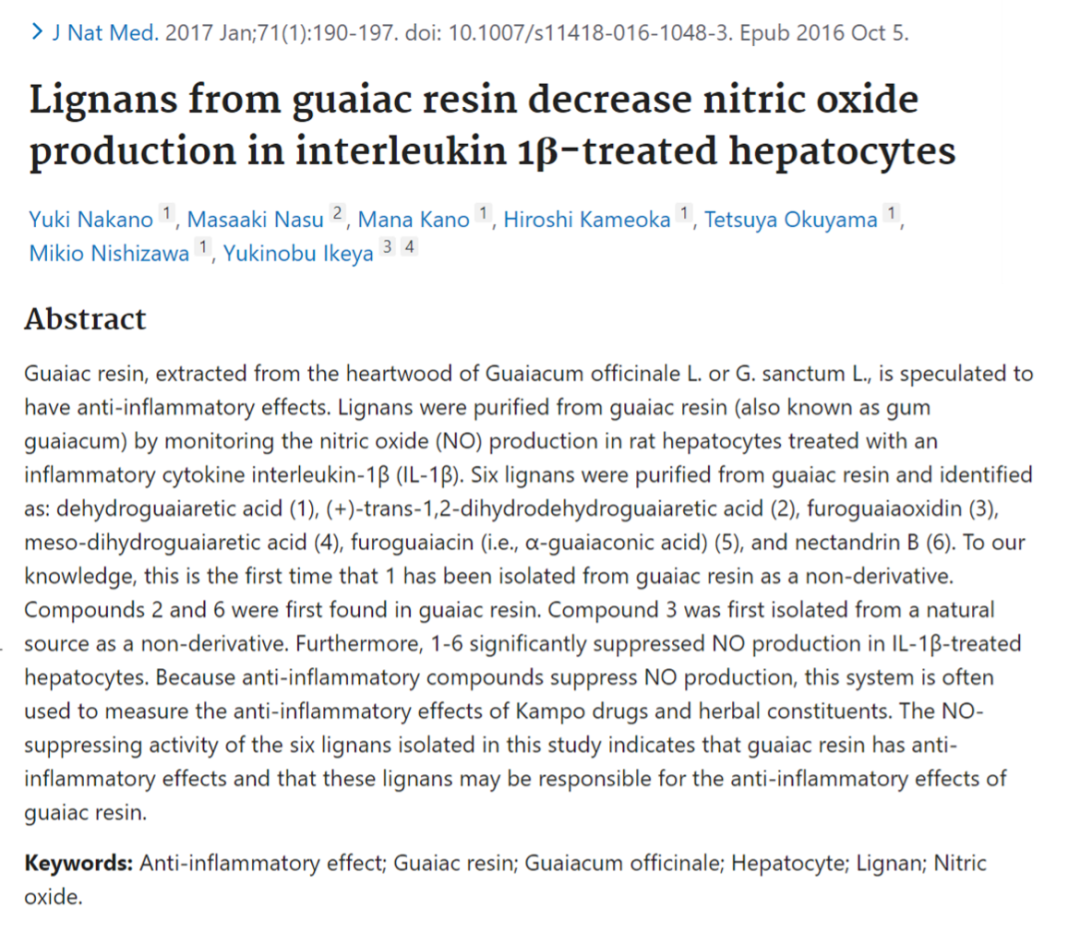
▸ 研究中分离的六种木脂素的NO 抑制活性表明愈创木树脂具有抗发炎作用,这些木脂素可能是愈创木树脂抗发炎作用的原因。
|原料认证
欲取得相关认证资料 请联系官方客服
▎参考文献
- Ouachinou JMS, et al. Variation of Secondary Metabolite Contents and Activities against Bovine Diarrheal Pathogens among Zygophyllaceae Species in Benin and Implications for Conservation. Planta Med. 2022. Mar;88(3-04):89.
- Bhatti UA, et al. Evaluating the impact of roads on the diversity pattern and density of trees to improve the conservation of species.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022. Feb;29(10):14780-14790.
- Ibrahim S, et al. Hepatoprotective and antidiabetic effect of Guaiacum officinale in diabetes induced male albino wistar rats. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2019.Tissandié L, et al. Towards a complete characterisation of guaiacwood oil.Phytochemistry. 2018. May;149:64-81.
- Nakano Y, et al. Lignans from guaiac resin decrease nitric oxide production in interleukin 1β-treated hepatocytes. J Nat Med. 2017.
- Tissandié L, et al. Revisiting the Chemistry of Guaiacwood Oil: Identification and Formation Pathways of 5,11- and 10,11-Epoxyguaianes. J Nat Prod. 2017. Feb 24;80(2):526-5 Nat Prod.
- Claudio-Campos K, et al. Biological screening of select Puerto Rican plants for cytotoxic and antitumor activities. PR Health Sci J. 2015. Mar;34(1):25-30.
- Sarkar A, et al. Anti-rheumatoid and anti-oxidant activity of homeopathic Guaiacum officinale in an animal model. Homeopathy. 2014. Apr;103(2):133-8.
- Saba N, et al. Separation and identification of a new saponin from the flowers of Guaiacum officinale L. Nat Prod Res. 2010. Dec;24(20):1877-82.
- Ahmad VU, et al. Triterpenoid saponin from the bark of Guaiacum officinale L. Nat Prod Res. 2004. Apr;18(2):111-6.10.Duwiejua M, et al. Anti-inflammatory activity of Polygonum bistorta, Guaiacum officinale and Hamamelis virginiana in rats. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1994. Apr;46(4):286-90. 11.Ahmad VU, et al. Guaiacum officinale. Planta Med. 1989. Jun;55(3):307-8
|部分图片来自网络,若有侵权请联系删除|