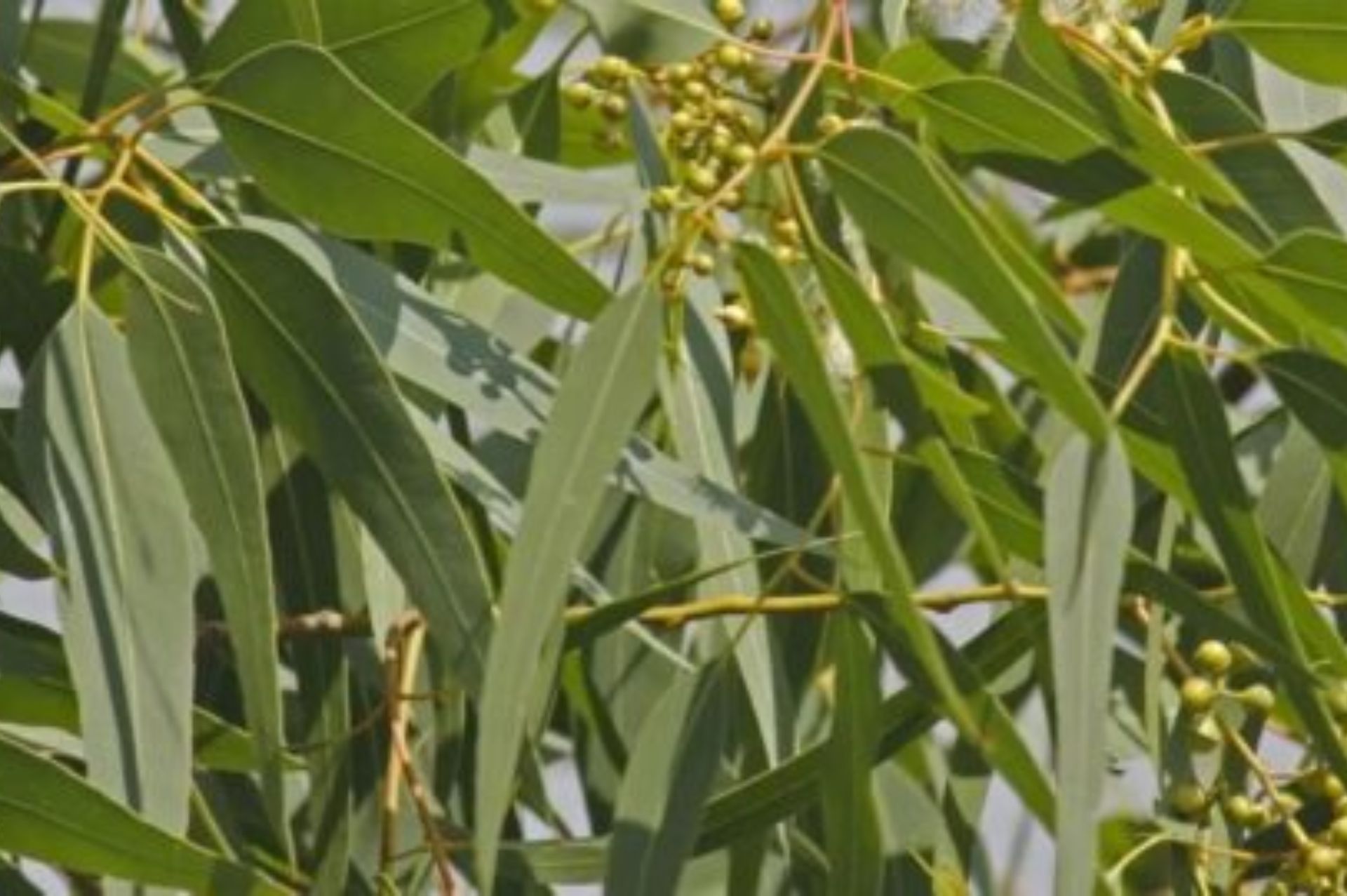
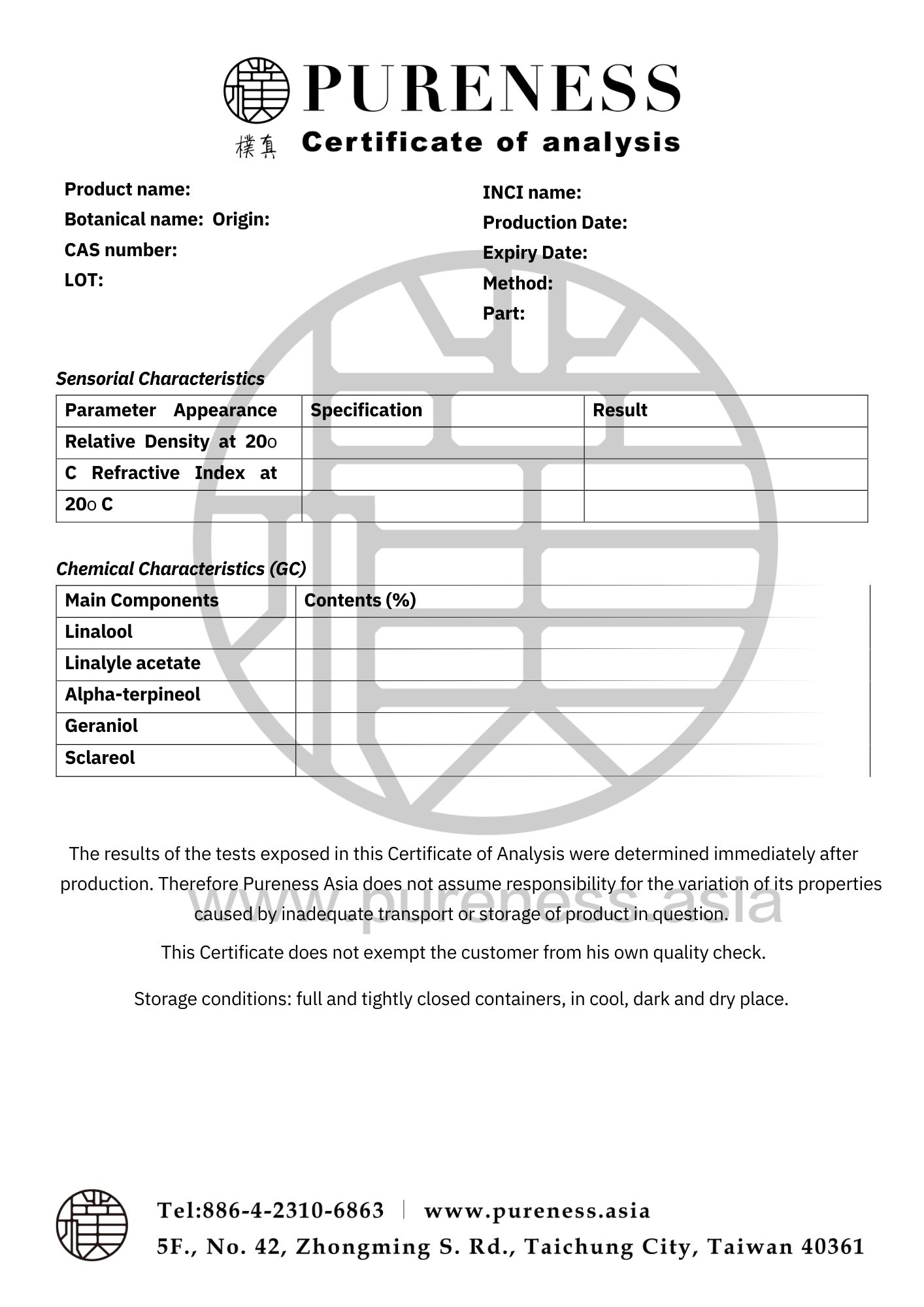
澳洲尤加利 Eucalyptus australia
拉丁学名|Eucalyptus radiata
主要产地|澳洲
原料分类|叶片系列
原料规格|500g-25kg 详情请咨询业务
萃取部位|叶片
萃取方式|蒸馏
植物科别|桃金娘科
植物气味|具轻盈畅快、提神醒脑的香气
▎精油简介
澳洲尤加利(Eucalyptus radiata),又称为桉树或俗称孤独树,它是澳洲木本植物中代表性的树种,一般为常绿乔木,数高达30m,整体树形成金字塔状,树皮为灰色纤维状,叶片较薄,叶子通常互生,有柄,全缘羽状脉,多为镰刀形;枝、叶、花有芳香;早春开白色、红色或黄色花,多为繖形或头状花序。同属的尤加利树由于适应澳洲各种不同的地理气候,其覆盖率遍及整个澳洲。
因生长速度很快,对水的需求量较大。因为尤加利树的经济价值与种植成活率较高,澳洲东部的30至50种尤加利树,为澳洲的代表树种,也是无尾熊的主要食物,看到尤加利就很自然地想到无尾熊抱吃的画面。
尤加利树本身带有的挥发性芳香油是许多蚊虫不喜欢的味道,是含氧率很高的一种精油,对于净化空气,清洁呼吸系统都有十分显著的效果。
▎成分解析
|主要成分:氧化物
澳洲尤加利含有高比例氧化物(1,8-桉油醇),同时还含有单萜醇、单萜烯、单萜酮等其他分子结构,所产生的协同作用具有一定医疗价值,如:α-蒎烯,柠檬烯,α-萜品醇,顺式胡椒醇,牻牛儿醇等。
|成分1:1.8-桉油醇 (1,8 cineole)
尤加利具有高含量的1,8-桉树脑,商业上可用于制药和化妆品工业中的精油生产。且被广泛种植用于纸浆,胶合板和实木的生产,其叶子芳香油具有令人震惊的广泛生物活性。

▸ 在研究中发现1.8-桉油醇,具有抗炎活性,因此在上呼吸道和下呼吸道疾病中可用作黏液溶解剂。
|成分2:右旋萜品烯-4-醇(Terpinen-4-ol)
要特别注意放置太久的萜品烯-4-醇会氧化成香荆芥酚,具皮肤刺激性。
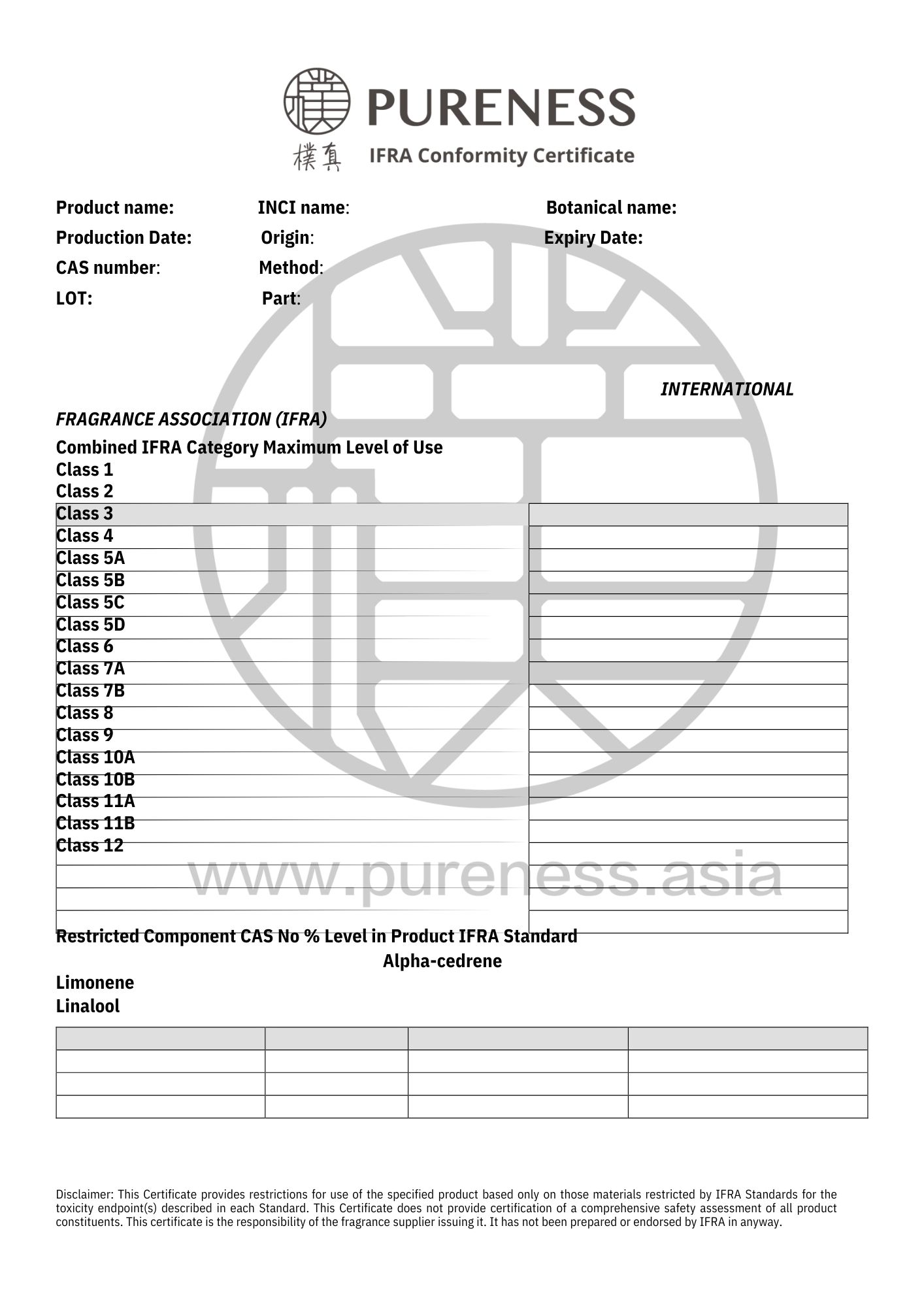
|原料认证
欲取得相关认证资料请咨询官方客服
▎参考文献
- Ashok K Dhakad et al. Biological, medicinal and toxicological significance of Eucalyptus leaf essential oil: a review. J Sci Food Agric. 2018 Feb;98(3):833-848.
- Bom Park , Eunson Hwang , Seul A Seo , Jin-Gyeong Cho , Jung-Eun Yang , Tae-Hoo Yi. Eucalyptus globulus extract protects against UVB-induced photoaging by enhancing collagen synthesis via regulation of TGF-β/Smad signals and attenuation of AP-1.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2018 Jan 1;637:31-39.
- Myburg et al. The genome of Eucalyptus grandis, Nature (2014), doi:10.1038/nature13308
- Elaissi A., Rouis Z., Salem N.A.B., Mabrouk S., Ben Salem Y., Salah K.B.H., Aouni M., Farhat F., Chemli R., Harzallah-Skhiri F. Chemical composition of 8 Eucalyptus species’ essential oils and the evaluation of their antibacterial, antifungal and antiviral activities. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2012;12:1.
- Cermelli C, Fabio A, Fabio G, Quaglio P. Effect of eucalyptus essential oil on respiratory bacteria and viruses. Curr Microbiol. 2008;56:89–92.
- Bennett, B.M. The El Dorado of Forestry: The Eucalyptus in India, South Africa, and Thailand, 1850–2000 55, Supplement 18 (2010): 27-50.
- Tyagi AK, Malik A. Antimicrobial potential and chemical composition of Eucalyptus globulus oil in liquid and vapour phase against food spoilage microorganisms. Food Chem. 2011;126:228–235.
- Blakely, W.F.A Key to the Eucalypts: with descriptions of 522 species and 150 varieties. Third Edition, 1965, Forest and Timber Bureau, Canberra.
- Boland, D.J.; M.I.H.; McDonald; M.W.; Chippendale; G.M.; Hall; N.; Hyland; B.P.M.; Kleinig; D.A. Forest Trees of Australia. Collingwood, Victoria: CSIRO Publishing. 2006. 5th edition. ISBN 0-643-06969-0
- Brooker, M.I.H.; Kleinig, D.A. Field Guide to Eucalyptus. Melbourne: Bloomings. 2006.Third edition. ISBN 1-876473-52-5 vol. 1. South-eastern Australia.
- Sartorelli P, Marquioreto AD, Amaral-Baroli A, Lima ME, Moreno PR. Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of the essential oils from two species of Eucalyptus. Phytother Res. 2007;21:231–233.
- Kelly, Stan, text by G. M. Chippendale and R. D. Johnston, Eucalypts: Volume I. Nelson, Melbourne 1969, 1982, etc.
- L'Heritier de Brutelles, C. L. Sertum Anglicum. Paris: Didot. 1789.
- Richard K. P. Pankhurst. Economic History of Ethiopia. Addis Ababa: Haile Selassie I University. 1968.
- Boland, D.J., Brophy, J.J., and A.P.N. House, Eucalyptus Leaf Oils, 1991, ISBN 0-909605-69-6
- FAO Corporate Document Repository, Flavours and fragrances of plant origin
- Cermelli C, Fabio A, Fabio G, Quaglio P. Effect of eucalyptus essential oil on respiratory bacteria and viruses. Curr Microbiol. 2008 Jan;56(1):89-92.
- Ács K, Balázs VL, Kocsis B, Bencsik T, Böszörményi A, Horváth G. Antibacterial activity evaluation of selected essential oils in liquid and vapor phase on respiratory tract pathogens. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018 Jul 27;18(1):227.
- Yang C, Hu DH, Feng Y. Antibacterial activity and mode of action of the Artemisia capillaris essential oil and its constituents against respiratory tract infection-causing pathogens. Mol Med Rep.2015 Apr;11(4):2852-60.
- Biedenbach DJ, Jones RN. Update of cefditoren activity tested against community-acquired pathogens associated with infections of the respiratory tract and skin and skin structures, including recent pharmacodynamic considerations. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2009 Jun;64(2):202-12.
- Hassan ST, Majerová M, Šudomová M, Berchová K. [Antibacterial activity of natural compounds - essential oils]. Ceska Slov Farm. 2015 Dec;64(6):243-53.
|部分图片来自网络,若有侵权请联系删除|